Artificial Intelligence (AI) and 2D/3D Geospatial Technology
The latest innovation to capturing precise and accurate geospatial data over large areas from aerial or satellite imagery has been the utilization of Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL) and Computer Vision (CV). AI and ML models have great success in many fields related to obtaining large amounts of image data to aid in pattern recognition and create algorithms through computer systems. AI and ML can help the end data user to understand the data collected in order to find resolutions to the focused project at hand, rapidly. AI can improve in the analysis of large areas of interest, to classify objects, detect and monitor land use, data fusion, cloud removal, and spectral analysis of environmental changes from satellite or aerial imagery.
Artificial intelligence and remote sensing can create Computer Vision models to better understand the data. Images collected by satellites or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV), these models can provide near real-time reports for large scale sized areas with complex feature distribution such as the transition of electric power grids to a digital twin, agriculture, urban planning, transportation, disaster management, climate change, and wildlife conservation. AI can aid in data collection, processing, and understanding using neural networks and deep learning through Computer Vision models to allow data users to better understand and handle data more efficiently in a timely manner, at spatial resolutions of 2cm through 15cm by Digital Aerial Photography and LiDAR, and from 15cm to 2.0m by a variety of Satellite sensors.
AI for Agriculture Applications
Statistics show that the world’s population will reach 9.1 billion by 2050. Due to this expected growth, there is pressure worldwide for higher agricultural production and reliable crop status information. To achieve these objectives, improved management of the world’s agricultural resources is required, especially in developing countries.
Utilizing high-resolution, multi-spectral satellite images and AI, ML, and CV algorithms, image data is collected and processed, extracting spectral analyzed data and transferred into management solutions for crop health and improved production targets.
AI and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) tools can help farmers to conduct crop forecasting and manage their agriculture production by utilizing image data collected by satellites, fix wing aircraft, or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV). This data is collected and processed to provide NDVI and many other vegetation indices to identify crop stress, waterlogging, manage production yields and tree grading. The ability of AI and GIS to analyze and visualize agricultural environments and workflows has proven to be very beneficial to those involved in the farming and agricultural industries.
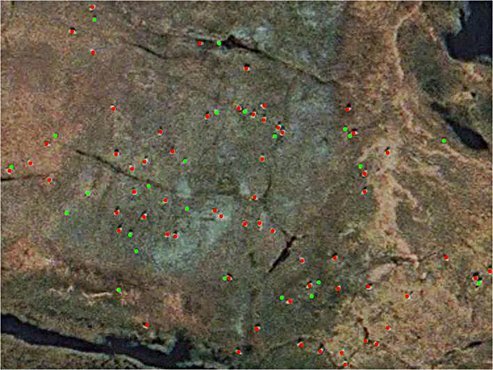
WorldView-3 Satellite Image (30cm)
Wildlife Monitoring, Caribou Herd Migration – North Slope of Alaska
Click image to view animation
Copyright © MAXAR/Processed by Satellite Imaging Corporation. All rights reserved.
AI for Wildlife Conservation
The latest innovation to aid in protecting and conserving the national parks has been from the utilization of AI and ML for wildlife conservation. AI for wildlife conservation takes advantage of ML and CV models. Using imagery collected by satellites or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) can predict behavior and provide near real-time reports of repetitive attacks by poachers that will assist anti-poaching teams in catching the offenders. This state-of-the-art technology enables scientists and conservationists to decrease illegal activities such as attacks on wildlife and natural resources.
AI applications are a great alternative to manual data collection, camera-trap imagery, or recording audio that can lead to days or even months of exhausting work. Using browser-based tools, programming libraries, and neural networks, AI augments conservation efforts by helping scientists and conservationists to detect and monitor wildlife by using satellite image data to help identify a particular species that can be closely monitored to help protect wildlife.
Consultancy
Ongoing Satellite remote sensing and GIS consultancy services are provided to our clients, including the set-up of reliable source coordinate databases in support of computerized mapping, exploration, and development of projects around the world and to clients implementing AI/ CV or GIS management systems, utilizing a variety of source data. For more information or for a consultation, please contact us.