Machine Learning (ML) and Remote Sensing Technology
Machine Learning (ML) and remote sensing technology aids in many applications requiring large amounts of spectral and spatial data needed for pattern recognition. ML uses algorithms through computer systems, computer vision, and deep learning methods to collect and identify features in an environment with precise accuracy and speed. ML a subdivision of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Computer Vision (CV) can help the end-user to understand the data collected in order to find resolutions for remote sensing data and improve the overall accuracy of the data classification and can enhance the reliability and assessment of the features of data collected. ML algorithms through neural networks can improve the analysis of large areas to classify objects, identify temporal change, data fusion, cloud removal, and spectral analysis from satellite or aerial imagery that will overcome challenges of remote sensing data.
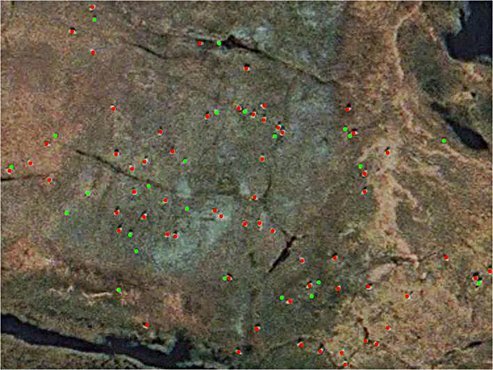
WorldView-3 Satellite Image of Caribou Herd Migration – North Slope of Alaska (30cm)
Click image to view animation
Copyright © MAXAR/processed by Satellite Imaging Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Images collected by satellites or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) by applying ML techniques, these models can provide near real-time reports for areas with complex feature distribution such as in the applications of environmental monitoring and management, mineral mapping, agriculture, disaster management, climate change, and wildlife conservation.
ML for Environmental Monitoring
Using standard VNIR/SWIR and Hyperspectral Satellite sensors, SIC can provide data with advanced spectral resolution and capabilities to detect carbon (CO2) and methane (CH4) emissions and monitor changes over time. Machine learning (ML) algorithms have proven to be a powerful tool to acquire remote sensing data at high processing speeds for applications involving environmental studies, land change detection, land use, agriculture, energy, climate change, and forestry.
ML for Habitat Mapping & Monitoring
Remote sensing, ML, and GIS, have greatly expanded opportunities for data collection, integration, analysis, and modeling for wildlife monitoring and assessment. High-resolution satellite images give scientists and researchers increasingly up-to-date geospatial and spectral data at high processing speeds through neural networks. Reliable statistics are obtained for monitoring wildlife migrations, habitat mapping, and tracking endangered species in remote areas of the world in order to assist with habitat mapping, wildlife monitoring, and wildlife conservation activities.
Spectral and spatial data are collected for wildlife monitoring and management by utilizing neural networks algorithms by acquiring data and statistics to obtain accurate and precise data for conservation projects. Remote sensing data and ML can provide data and features in support of habitat mapping, migrations, illegal activities, and monitoring changes in forest cover. This method allows scientists, researchers, and conservationists to collect and analyze data in a time-sensitive series that can allow estimated rates and patterns of remote wildlife areas.
Consultancy
Ongoing remote sensing and GIS mapping consultancy services are provided to our clients, including the set-up of reliable source coordinate databases in support of computerized mapping, exploration, and development of projects around the world and to clients implementing AI, CV and GIS management systems, utilizing a variety of source data. For more information or for a consultation, please contact us.