Flood Risk Management
Stereo and Tri-Stereo satellite imagery and high-resolution Digital Terrain Models (DTMs) are invaluable tools in flood risk management, providing essential data for assessing natural hazards, environmental monitoring, and climate change impacts.
Flood Risk Hazard Assessment and Monitoring
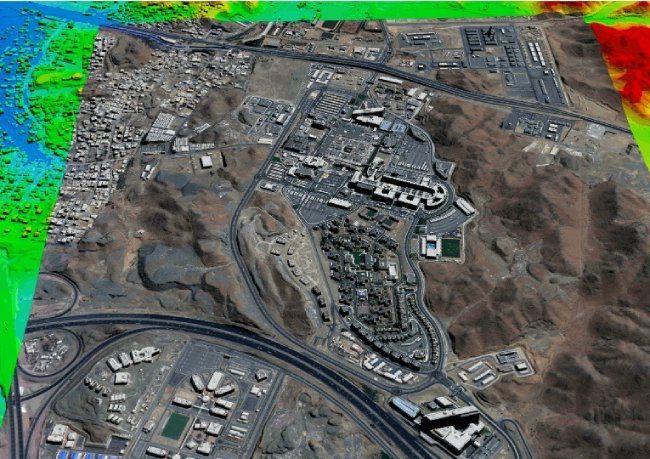
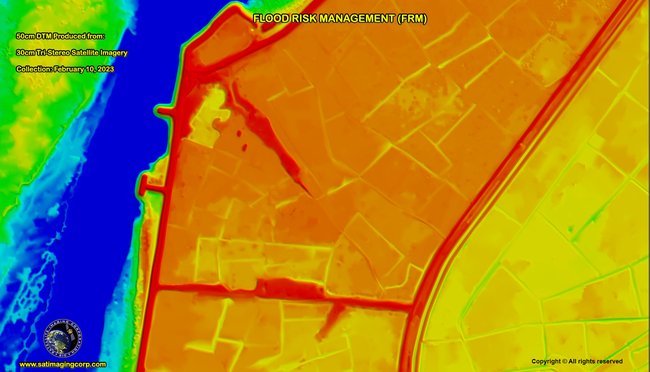
Satellite images can help detect flooded areas during and after flood events. They allow for quick identification and assesment of affected regions and the extent of floodwaters, critical for response and damage assessment. DTMs offer precise elevation data that is crucial for mapping flood-prone areas. By hydrological modeling how water moves across terrain, DTMs help identify low-lying regions more likely to flood, aiding in early warning and planning.
Flood Risk Assessment and Planning
Integrating DTM data with historical flood patterns from satellite imagery enables detailed flood risk maps. These maps highlight vulnerable infrastructure, residential zones, and ecosystems, allowing planners to assess risks and prioritize protective measures.
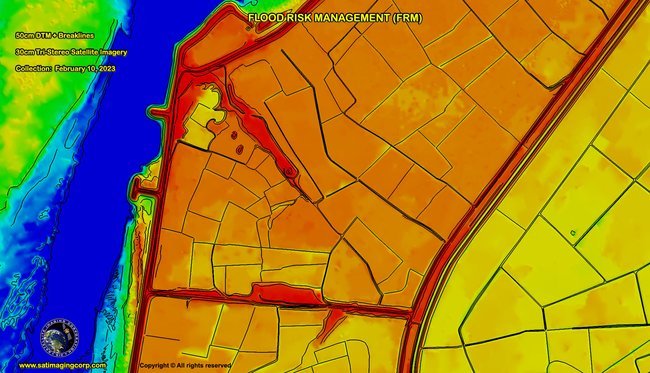
DTMs with breaklines are integral to flood modeling. By combining terrain data with hydrological models, planners can simulate flood events and predict water levels under various scenarios. These simulations support the design of effective flood barriers, drainage, and urban planning that minimizes flood impact.
Click on image to view the video.

Copyright © Satellite Imaging Corporation. All rights reserved.
Detailed imagery is used for flood risk planning with the availability of High-Definition (HD) 15cm imagery produced from 30cm satellite imagery and proprietary AI algorithms developed by MAXAR and AIRBUS.
Monitoring Environmental Change and Climate Impact
Over time, satellite images reveal shifts in river courses, coastline erosion, and snow and ice cover changes. Monitoring these trends provides insights into how climate change affects flooding patterns, helping authorities anticipate areas that may experience increased risk.
Satellite images track land cover changes, such as urbanization and deforestation, which can exacerbate flood risks. Loss of vegetation reduces the ground’s ability to absorb water, increasing runoff and flood potential. Monitoring these changes informs sustainable land management practices.
Disaster Response and Recovery
During flood events, satellites continuously monitor the affected areas in real-time, updating flood models and helping responders plan evacuations, allocate resources, and prioritize rescue operations. In the recovery phase, they aid in assessing damages identified by temporal satellite imagery, change detection AI/ML processing algorithms, and restoring impacted ecosystems.
High-resolution satellite imagery and DTM data allow post-flood analysis to evaluate the effectiveness of flood defenses, infrastructure resilience, and recovery efforts, which can improve future flood risk management. Satellite imagery and DTMs support a proactive approach to flood management by enabling accurate risk mapping, real-time response, and long-term planning for climate resilience.
World Bank Urban Flood Risk Handbook: Assessing Risk and Identifying Interventions
The World Bank Urban Flood Risk Handbook is a guide aimed at helping cities and governments to better understand and mitigate urban flood risks. Urban flooding is a critical issue in many parts of the world, intensified by rapid urbanization and climate change, leading to more frequent and severe flooding. The handbook is designed to provide a framework for assessing flood risks in urban areas and offers actionable guidance on how to manage and reduce these risks effectively.
Importance and Impact
The handbook is valuable for urban planners, engineers, policymakers, and community leaders, especially in developing countries where resources. By following this guide, cities can work toward reducing flood vulnerability, protecting lives and property, and building resilience against future climate-related challenges. The World Bank’s approach in this handbook also aligns with its broader goals of poverty reduction and sustainable urban development, emphasizing that flood management is critical for both economic growth and environmental stability.