EXPLORACIÓN MINERAL Y MINERÍA
Las Imágenes de satélite y la fotografía aérea han demostrado ser herramientas importantes en el apoyo de proyectos de exploración mineral. Se pueden usar en una variedad de formas. Primeramente les suministran a los geólogos y equipos de campo la localización de senderos, carreteras, cercas y áreas inhabitadas. Esto es importante para elaborar mapas de corredores de acceso potencial para áreas de exploración y para considerar el impacto sobre el medio ambiente de proyectos mayores. Estas imágenes también son útiles para la preparación de mapas de afloramientos de rocas y sistemas de regolitos como también cobertura de vegetación a través de bloques de exploración y sobre áreas regionales.
Las imágenes de satélite pueden también beneficiar a geólogos, científicos, y administradores de exploración gracias a las bandas múltiples que los satélites utilizan, que les permiten interpretar longitudes de onda que no se pueden ver con el ojo humano. Cerca de infrarrojo, infrarrojo de onda corta, e infrarrojo térmico pueden usarse para identificar la diferencia en aspectos característicos de la superficie terrestre.
Imágenes multi-espectrales y mapas temáticos les permiten a los investigadores recolectar datos de reflexión y propiedades de absorción de suelos, rocas y vegetación. Estos datos pueden ser utilizados por fotogeólogos peritos en la interpretación de litologías de superficies e identificación de arcillas, óxidos, y tipos de suelos por medio de las imágenes de satélites.
el mio en
solución salina, california
Valle Saline Mineral Maps, California
Imagen de Satélite ASTER (15m)
En el ejemplo de arriba, la imagen de la izquierda muestra bandas visibles y cerca de infrarrojas 3, 2, y 1 en rojo, verde y azul (RVA). La vegetación aparece roja, la nieve y los lagos de sal seca son blancos, y las rocas expuestas son café, grises, amarillas y azules. Los colores de las rocas pueden reflejar la presencia de minerales de hierro y variaciones de albedo. La imagen del centro muestra bandas infrarrojas de longitud de onda corta 4, 6, y 8 como RVA. En esta región de longitud de onda, arcilla, carbonato, y minerales sulfatos tienen características de absorción diagnósticas que resultan en colores distintos en la imagen. Por ejemplo, las piedras calizas son verde-amarillas y las zonas moradas son ricas en kaolinita. La imagen derecha muestra bandas infrarrojas térmicas 13, 12 y 10 como RVA. En esta región de longitud de onda, variaciones en contenido de cuarzo aparecen como más o menos rojas; las rocas carbonatas son verdes, y las rocas volcánicas ricas en magnesio y hierro son moradas.
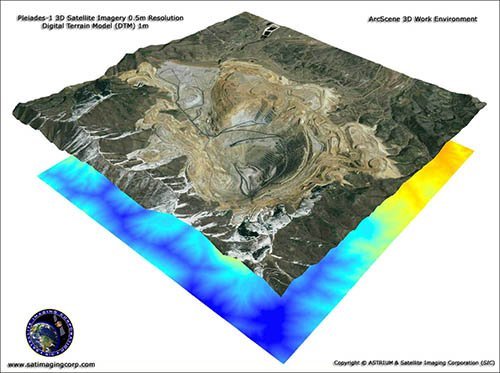
Imagen de Satélite Pleiades-1A (0.5m)
Mina de Cobre del Cañón Bingham – Utah,USA
Copyright © AIRBUS Defence & Space.
La Corporación de Imágenes de Satélite (Satellite Imaging Corporation – SIC) suministra imágenes de satélite de alta resolución para análisis y aplicaciones de elaboración de mapas tales como el Sistema de Información Geográfico (Geographic Information System – GIS). Nuestra producción de imágenes, Sistema de Información Geográfico (GIS), Sistema de Posicionamiento Global (GPS), y expertos en geodesia tienen vasta experiencia en procesamiento de imágenes, ortorrectificación, georreferencias, extracción de características, y elaboración de mosaicos para las necesidades específicas de su proyecto.
Además trabajamos con consultores peritos en geología y podemos utilizar sus conocimientos para interpretar los datos de imágenes para diferentes aplicaciones en minería y geología.
Si usted tiene en particular un proyecto geológico o sobre minería nos complacería revisar sus requisitos y darle un estimativo sobre lo que podemos suministrarle en apoyo de su proyecto.
Imágenes de muestra
Exploración, clasificación e interpretación de minerales
* Click on thumbnail to view in full resolution.
Para muchas solicitudes de imágenes, se puede localizar una imagen correspondiente en nuestros archivos globales de imágenes de satélite. Si ninguna imagen estuviese disponible en los archivos, se pueden adquirir nuevas imágenes de satélite a través de un proceso de trabajo por medio de satélite. Además de suministrar datos sobre imágenes, la Corporación de Imágenes de Satélite (Satellite Imaging Corporation) realiza muchas labores en su trabajo de fondo para asegurar que cumplamos las especificaciones y los requisitos de horario del cliente.
- Negociar la consecución de imágenes
- Procesar imágenes, incluyendo ortorrectificación, DSM, DTM, y conversiones de escalares de atributos a vectores
- Suministrar visualización de terreno en 3D y modelar para planeación y asistencia técnica de proyectos
- Incorporar información de GIS de partes terceras
- Consultar sobre combinaciones de bandas más apropiadas para resaltar las características geográficas y las hechas por el hombre que sean más apropiadas para su proyecto
- Realizar análisis espectral para clasificaciones del uso de la superficie terrestre y cambios en el impacto sobre el medio ambiente
Suministrar visualización de terreno en 3D y modelar para planeación y asistencia técnica de proyectos Incorporar información de GIS de partes terceras Consultar sobre combinaciones de bandas más apropiadas para resaltar las características geográficas y las hechas por el hombre que sean más apropiadas para su proyecto Realizar análisis espectral para clasificaciones del uso de la superficie terrestre y cambios en el impacto sobre el medio ambiente.
Información sobre imágenes de satélite ha sido utilizada tanto por el gobierno como por comunidades comerciales, industriales, civiles, y educativas a través del mundo. La información se usa para respaldar una gran gama de aplicaciones en áreas tales como investigación sobre cambio global, agricultura, ciencias forestales, geología, manejo de recursos, geografía, elaboración de mapas, hidrología, y oceanografía.
La Corporación de Imágenes de Satélite está disponible para asesoría en sus necesidades de imágenes y elaboración de mapas de sus proyectos. Por favor contáctenos para cualquiera pregunta.