Con el aumento en la presión de población por todo el mundo y la necesidad de una producción agrícola creciente existe una necesidad definida de una mejor administración de los recursos agrícolas del mundo. Para que esto suceda es necesario en primer lugar obtener datos fiables de no solamente los tipos, sino también la calidad, cantidad y ubicación de estos recursos. La tecnología satelital o aérea de Detección Remota (RS por sus siglas en inglés) ha sido y siempre continuará siendo un factor muy importante en la mejora de los sistemas presentes de adquirir y generar datos agrícolas y de recursos.
Evaluación administrada de la cubierta vegetal

Copyright © DigitalGlobe. All rights reserved.
Se están llevando a cabo en la actualidad encuestas agrícolas por todo el mundo a fin de recoger información y estadísticas de cosechas, praderas, ganado y otros recursos agrícolas relacionados. Esta información de datos es muy importante para la implementación de decisiones eficaces de administración. La encuesta agrícola es necesaria para planificar y asignar los limitados recursos a diferentes sectores de la economía.
Satellite Imaging Corporation proporciona datos de imágenes satelitales a diferentes resoluciones espaciales, espectrales y temporales para la evaluación agrícola y de cultivos, salud de los cultivos, detección de cambio, análisis ambiental, , cartografía de regadío, determinación de rendimiento y análisis de suelos. La programación y el momento de la adquisición de la imagen son muy importantes y dependerán de los objetivos principales y del tipo de información que el usuario final espera conseguir. Las imágenes pueden mostrar variaciones en los patrones de material orgánica y drenaje. Suelos con un alto contenido de materia orgánica pueden diferenciarse de suelo arenoso más claro que tiene un contenido de materia orgánica más bajo. Esta información geoespacial es valiosa cuando se usa conjuntamente con datos complementarios para definir zonas de administración para un campo. Una vez que se han recogido los datos, pueden implementarse en un ambiente cartográfico tal como GIS (Sistema Geográfico de Información) para la administración y control de recursos agrícolas.
Analisis de Vegetacion
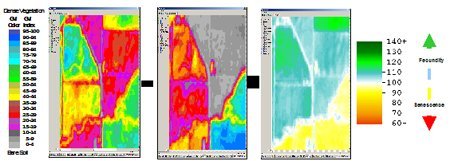
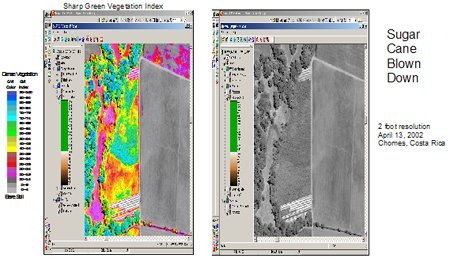
Imágenes de vegetación — muestran crecimiento de cultivo desde la siembra a la cosecha, cambios a medida que las estaciones progresan y anormalidades tales como terrenos de malas hierbas, compresión del suelo, problemas de riego, etc. Una imagen georeferenciada y ortorrectificada puede localizar estas áreas problemáticas y puede determinarse fácilmente también el tamaño del área afectada. Esta información puede ayudar al granjero a tomar decisiones informadas acerca de la solución más factible. Además de realzar áreas problemáticas, las imágenes ayudarán a controlar la eficacia de cualquier acción correctiva que pueda implementarse. Las imágenes pueden actuar como un indicador temprano del rendimiento de la cosecha. Este indicador temprano de rendimiento puede ayudar al granjero a tomar decisiones de marketing así como a la asignación de recursos.
Para ganar beneficios de datos detectados a distancia, los granjeros, gerentes, consultores y técnicos deben entender y ser capaces de interpretar la imagen. Existe una amplia gama de herramientas de realce disponibles que pueden ayudar a hacer una mejor interpretación de una imagen para aplicaciones específicas. A menudo se usan herramientas de realce y clasificación para poner de relieve características. Las técnicas empleadas dependerán del tipo de datos de detección a distancia así como de los objetivos del usuario final. Las técnicas comúnmente usadas incluyen:
Detección de cambio — o estudio de cambios de vegetación restando una imagen de otra imagen adquirida anteriormente.
Copyright © DigitalGlobe. All rights reserved.
AGROWATCH™
Clasificaciones — donde los pixeles de una imagen se clasifican en clases y a cada clase se le da un color único definido por las “firmas” espectrales. Una clasificación supervisada requiere conocimiento de los datos a medida que el analista selecciona pixeles que corresponden a características conocidas (tales como diferencias en la cobertura vegetal). Clasificaciones no supervisadas son más automatizadas por computadora y agrupan pixeles que tienen características espectrales similares. Muchas compañías usan este enfoque para producir una imagen de un campo con numerosos niveles de color de 8-15 que corresponden a área vegetal o masa de plantas.
Copyright © DigitalGlobe. All rights reserved.
Índices de vegetación — Usando la firma espectral distintiva de plantas con reflectancia baja en la zona visible (0.4-0.7 um) y muy alta reflectancia en la región cercana al infrarrojo (0.7-1.2 um) del espectro solar, el contraste espectral puede usarse para identificar la presencia de vegetación verde y evaluar algunas características a través de varios índices de vegetación, tales como el Índice Normalizado de Diferencia de Vegetación (NDVI).
Copyright © DigitalGlobe. All rights reserved.
Respuesta de la vegetación al riego

Copyright © DigitalGlobe. All rights reserved.
Satellite Imaging Corporation utiliza y proporciona técnicas avanzadas de detección remota, servicios de procesado de datos de imágenes en color y pancromáticas, incluyendo ortorrectificación, definición de tomas panorámicas con fusión de datos de imágenes, georeferenciación, mosaicos y equilibrado de color/escala gris para GIS y otras aplicaciones cartográficas.
SIC está disponible para consultoría de todas las necesidades y especificaciones de su proyecto. Usted puede contactarnos por Internet o telefoneando al +1 (832) 237-2900.



