ÍNDICE DE VEGETACIÓN VERDE:
UN MAPA DE LA SALUD DE LA VEGETACIÓN
Tomando mejores decisiones más rápidamente
Teniendo que considerar las variables del tiempo, medio ambiente y producción, la única cosa con la que los agricultores pueden contar es la incertidumbre. El tener una información integral actualizada de cada campo es crucial para optimizar sus estrategias de administración de cultivo en la estación.
Elementos centrales de la línea de productos AgroWatch™, los mapas de Índices de vegetación verde son imágenes detalladas que dan a los agricultores una medida absoluta de la cantidad de vegetación verde presente en sus campos. Estos mapas muestran los resultados integrados de datos de entrada y factores ambientales, físicos y culturales que afectan su cultivo. Con nuestros datos calibrados, usted puede evaluar la cantidad de vegetación de forma rutinaria y cuantitativamente, el estado y variación en sus tierras desde suelo desnudo a una densa cubierta forestal, para administrar mejor sus cultivos esta estación e ir hacia atrás en el tiempo para identificar factores limitadores de rendimiento.
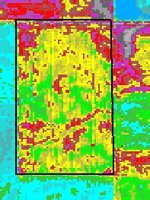
El captar perspectivas generales de grandes áreas de producción con una resolución de detalle de 30 pies, los mapas de Vegetación verde de AgroWatch™ también muestran tendencias a través de múltiples granjas. Para realzar sus decisiones en la estación, el programa de imágenes recoge datos a horas predefinidas y le entrega los mismos a usted en Internet en casi tiempo real. Los mapas de Vegetación verde son una importante herramienta realzadota de ingresos que le muestra dónde explorar y tomar muestras, el grado y severidad de áreas problemáticas y dónde aplicar datos de entrada, productos de protección de cultivos, reguladores de crecimiento o exfoliantes.

Una medida estandarizada del estado de los asuntos
Los mapas de Índice de vegetación verde AgroWatch™ le proporcionan una imagen completa y precisa de la cantidad de vegetación y variabilidad sin errores causados por el suelo y la humedad. Para crear un mapa de Índice de vegetación verde utilizando la tecnología de detección remota, Imágenes satelitales de alta resolución recogidas por sensores satelitales como GeoEye-1, WorldView-2, Pleiades-1, QuickBird, IKONOS y SPOT-6, son calibradas usando sus cultivos y se aplican algoritmos espectrales especialmente desarrollados para separar la reflectancia de la vegetación de la variación causada por suelos o agua subyacente. Al ofrecer una perspectiva transparente del estado actual de sus cultivos, el Índice de vegetación verde es una medida repetible que puede aplicarse consistentemente a través de varios escenarios, lugares de muestra e intervalos de tiempo. Agricultores, consultores y científicos pueden relacionar fácilmente el Índice de vegetación verde con medidas de vegetación estándar en la industria, tales como el índice del área de hojas verdes, altura de plantas, biomasa o porcentaje de cubierta forestal.
El resultado final es datos cuantificables que muestran el estado vegetativo de cada campo que usted puede usar para identificar tendencias locales, regionales o mundiales, rápida y exactamente. Puesto que los mapas están calibrados, pueden usarse para generar mapas de aplicación o bien en paquetes GIS de escritorio o a través de soluciones en línea suministradas por Satellite Imaging Corporation.
Ver donde no puede caminar
El Índice de vegetación verde AgroWatch™ es único en su habilidad de ayudar a usuarios a detectar problemas potenciales en cultivos densos en los que no puede caminar. Otros índices no pueden medir diferencias vegetativas una vez que la cubierta de cultivo cubre el suelo. Con el Índice de vegetación verde AgroWatch™ usted puede ver lo que está sucediendo en áreas a las que no tiene acceso. Con la ayuda de mapas de Índice de vegetación verde, agricultores, gerentes, asesores y consultores están tomando decisiones de cultivo más rápidamente, mejorando la calidad del cultivo y aumentando la productividad.
Índice de vegetación verd — De un vistazo
Qué: Mapas de color codificados muestran la cantidad de vegetación verde, variaciones en densidad de vegetación y la salud general de la planta. El color gris indica el suelo desnudo. La densidad de vegetación aumenta a medida que el color cambia de rojo a amarillo y a verde. Los colores azules indican la vegetación más den
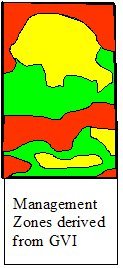
Usos: El Índice de vegetación verde AgroWatch™ muestra variaciones en un campo o región rápida y cuantitativamente, el grado de severidad de problemas que afectan al crecimiento vegetativo y dónde tomar muestras. Cuando se desee, el mapa GVI puede usarse para crear zonas de administración o mapas de Aplicación a Ritmo Variable (VRA por sus siglas en inglés).
Beneficio: Es más rápido, le ayuda a tomar mejores decisiones y reduce su compromiso de tiempo. Los usuarios de este producto pueden reducir su tiempo en cada campo al menos en un 30% mientras mejoran los resultados y aumentan las comunicaciones con los clientes.
AgroWatch™ es una marca registrada de DigitalGlobe.
SIC está disponible para consultoría de todas las necesidades y especificaciones de su proyecto. Usted puede contactarnos por Internet o telefoneando al +1 (832) 237-2900.



