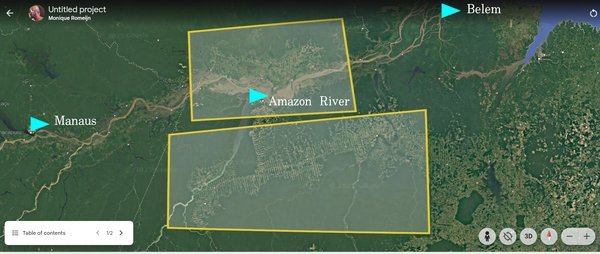
Deforestation in the Amazon Rainforest
The Amazon Rainforest is critical in regulating global climate change, preserving biodiversity, and sustaining indigenous and local communities. The Amazon is often referred to as the “lungs of the Earth,” and the effects of deforestation have been driven by illegal logging, agriculture for cattle ranching, illegal mining, and infrastructure development. The deforestation area most affected is between the cities of Manaus and Belém along the Amazon River in Brazil. The deforestation of this area is biodiversity loss, ecosystem disruption, soil erosion, greenhouse gas emissions causing climate change, and Indigenous community encroachment. The deforestation has critical levels, the loss of vital forest areas not only threatens biodiversity and the ecosystem but reduces carbon sequestration that accelerates climate change by releasing significant amounts of carbon (CO2) into the atmosphere.
Amazon Deforestation – Manaus and Belém, Brazil
Deforestation contributes to the disruption of weather patterns, water cycles, and endangering countless species including local communities. We need to find sustainable solutions to the urgency of the effects of deforestation. Researchers, government, and environmental organizations need to continue to explore and work on more effective mitigation and sustainable strategies for example, enforce laws, use innovative technologies, and practice regenerative agriculture techniques to rebuild and regrow and find long-term solutions. Traditional conservation and mitigation efforts have been a challenge in the past with the current rate of deforestation.
Today, innovative technologies and methods such as remote sensing using earth observation satellites, LiDAR, geographic information systems (GIS), artificial intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) have changed how we manage and monitor deforestation. Today, these tools currently assist in monitoring, preventing, and reversing environmental damage and support researchers and governments to address deforestation and climate change.
The effectiveness and application of the current technologies are highly dependent on local governments, environmentalists, and conservationists in the specified region to find strategies to slow down or reverse deforestation. Advancements in remote sensing using satellite imagery from earth observation satellites or LiDAR, GIS, AI, ML, and UAV, have significantly enhanced the capacity to monitor, manage, and detect deforestation and illegal activities in the Amazon. New technologies using AI monitoring systems can identify sounds associated with illegal deforestation, such as engines and motorized equipment that can analyze the rate of deforestation. The ML approach using neural networks can analyze LiDAR and satellite imagery to detect the areas mostly affected by deforestation local or in remote areas. ML can monitor and collect data in areas to locate permanent and temporary forest that are predictors of deforestation, and aid in analyzing and mitigating deforestation. The integration of GIS with satellite imagery or LiDAR, and AI has notably enhanced the monitoring and understanding of deforestation in the Amazon. These tools not only support in the detection of deforestation, but also provide data to manage the causes and effects of deforestation patterns, drivers, and give us potential mitigation strategies to find areas in need of intervention.
As of April 2025, several strategies are being actively implemented to reduce deforestation in the Amazon rainforest. We need to involve government and law enforcement policies, technological advancements, and international collaboration.